Madhya Pradesh Geography
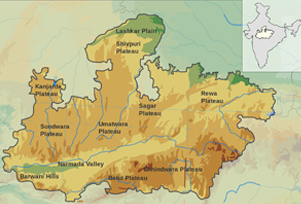
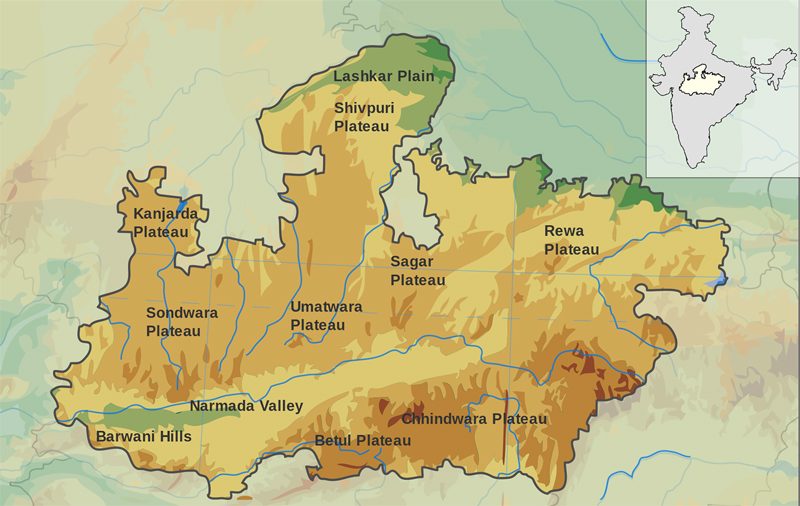
Madhya Pradesh means "central province', a region located at middle of the country.
Rivers like Narmada, Ken, Son, Tapi, Chmbal, Chambal flow through the state. The river Narmada flows from east to west in the state and in between Vindhya and Satpura ranges.
Wheat, maize, paddy, jowar, cereals, groundnut, mustard, cotton, sugarcane are some of the crops being produced in the state.
Vindhya range, Satpura range, Kaimur hill, Maikala range, Malwa plateau, Mahadeo hills, etc. are some of the mountains in the state. The total irrigation land in the state as per the official figures is 6.19 million hectares. Subtropical climate prevails in most part of the state. The heat is high during summer and the temperature is too low during winter.
Madhya Pradesh has the average rainfall of 1,370 mm. The rainfall is heavy in south eastern districts. The state has rich forest area. The total forest area of the state is 95,221 sq.km. It is 31 % of the geographical area of the state. Madhya Pradesh constitutes about 9.38 % of the total area of the country.
 The state is the second largest state in the country in terms of area. A typical feature of the state is that the state contains rivers, forests, plateaus, plains, hills, etc.
Based on the climate of the state, the state can be divided into the following regions. They are :
The state is the second largest state in the country in terms of area. A typical feature of the state is that the state contains rivers, forests, plateaus, plains, hills, etc.
Based on the climate of the state, the state can be divided into the following regions. They are :
- Northern Plains
- Malwa Plateau
- Mountainous Region of Bastar
- Narmada Valley
- Hilly Region of the Vindhyas
National Parks in Madhya Pradesh :
- Bandhavgarh National Park
- Fossil National Park
- Kanha National Park
- Madhav National Park
- Panna National Park
- Pench National Park
- Sanjay National Park
- Van Vihar National Park
- Satpura National Park