Uttarpradesh Economy
After long neglect and decay since Independence, Uttar Pradesh is getting things in order. CM Akhilesh Singh from Samajwadi Party has been proactive to woo investors, tourists, businessmen and intellectuals to make UP what it originally was -- a most progressive region in the whole subcontinent.
UP is a favoured tourist destination in India due to the location of Taj Mahal, one of the eight wonders of the world, in Agra. In 2014-15, the state was ranked second and third in terms of attracting domestic and foreign tourists respectively.
Nearly 182.8 million domestic and 2.9 million foreign tourists visited the state during the 2014-15. The huge northern state is the second largest producer of vegetables in the country.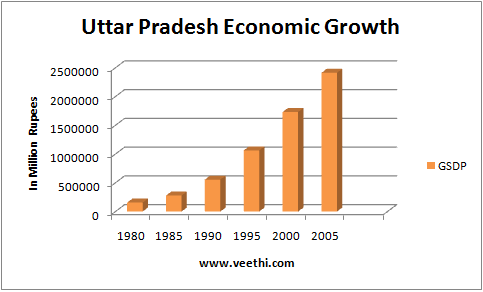
It produced over 21.47 million tonnes of vegetables in 2014-15. Uttar Pradesh is also the largest milk producing state accounting for nearly 17% of the total milk produced in the country in 2014-15.
Owing to the state’s large base of skilled labourers, it has emerged as a key hub for IT and ITeS industries, including software, captive business process outsourcing (BPO) and electronics.
The state has become a hub for the semiconductor industry with several major players having their offices and R&D centres in Noida. UP offers a wide range of subsidies and fiscal incentives as well as guidance for businesses under the Industrial and Service Sector Investment Policy 2004 and Infrastructure and Industrial Investment Policy 2012.
The state has well-drafted, sector-specific policies for IT and biotechnology. In the 2015-16 Budget, the state government has proposed an investment of $50.3 billion for enhancements in power, health and transportation sectors.
The gross state domestic product (GSDP) of Uttar Pradesh was $161.10 billion in 2014-15.The state’s per capita GSDP in 2014-15 was $755 compared with $326.3 in 2004-05.
Key drivers of economy
Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in India, with a large pool of skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labour. Alternately, the population is also looked upon as the largest consumer base in the country with around 200 million people.
 The state’s resources, policy incentives, infrastructure and climate are best suited for investments in diverse sectors such as IT, agro-based and food processing, light engineering goods, sports goods, textiles, leather-based, tourism and biotech.
The state’s resources, policy incentives, infrastructure and climate are best suited for investments in diverse sectors such as IT, agro-based and food processing, light engineering goods, sports goods, textiles, leather-based, tourism and biotech.
UP has a well-developed social, physical and industrial infrastructure. It also has good connectivity through 48 national highways, six airports and rail links to all major cities. The state has witnessed a high rate of infrastructure growth in the recent past.
There has been a considerable rise in the number of industrial clusters and public-private-partnership (PPP) projects in the infrastructure domain. The Uttar Pradesh State Industrial Development Corporation (UPSIDC) and the Department of Infrastructure and Industrial Development are responsible for the development of industrial infrastructure in the state.
The state has a robust infrastructure for economic growth including 15 industrial areas, 12 specialised parks, four growth centres and industrial infrastructure development centres (IIDC).
As of March 2015, the state had 18 notified special economic zones (SEZs). As per the 12th Five-Year-Plan (2012-17), the state’s industrial growth rate is expected to average 11.2% per annum.
Major government initiatives
Some of the major initiatives taken by the government to promote Uttar Pradesh as an investment destination are:
- The state offers a wide range of subsidies, policy and fiscal incentives as well as assistance for businesses under the Industrial and Service Sector Investment Policy, 2004 and Infrastructure & Industrial Investment Policy, 2012.
- The state has well-drafted, sector specific policies for IT and biotech.
- The state government has set up Udyog Bandhu to facilitate investment in industrial and service sectors.
- The organisation has a three-tier structure with presence at district, divisional and state levels.
- The government of Uttar Pradesh has sanctioned 22 SEZs across the state, such as IT and ITeS, electronic hardware and software, handicrafts and agro-based industries.
- The state has proposed 40 IT/ITeS parks (apart from IT SEZs), two biotech zones and a knowledge park.
- Development of integrated agro/food processing zones has been proposed at Hapur, about 54 km from Delhi.
- An apparel park at Tronica City, Ghaziabad, and a textile and hosiery park at Rooma in Kanpur district have been set up by UPSIDC to promote the apparel industry.
Biggest consumer market
From 2011 to 2015, Uttar Pradesh has shown a decent rate of growth of more than 6%, with a rapidly growing industries and services sector which has made it anattractive state for trade and investments.
 Agriculture and service industries form the largest parts of the state's economy. The service sector comprises travel and tourism, hotel industry, real estate, insurance and financial consultancies. The state is the second largest producer of sugarcane in the country.
Agriculture and service industries form the largest parts of the state's economy. The service sector comprises travel and tourism, hotel industry, real estate, insurance and financial consultancies. The state is the second largest producer of sugarcane in the country.
UP is one of the most favoured tourism destinations and was ranked second and fourth in terms of domestic and foreign tourists respectively in 2013. The state has the third highest number of micro, medium and small enterprises (MSMEs) in the country.
With an investment of over $4 billion, over 1,75,000 MSME units were set up during the11th Five-Year-Plan (2005-12). It has emerged as a key hub for IT and ITeS industries including software, captivebusiness process outsourcing (BPO) and electronics. The per capita income of the state is increasing steadily, leading to the origin of the biggest markets for industrial houses.
Tremendous opportunities exist in the areas of software and electronics fields as the state is attracting foreign direct investment. UP provides a large resource base of skilled labour which makes it an ideal destinationfor knowledge-based sectors. The state offers attractive subsidies, fiscal sops and time-bound clearances as well as expert guidance for investors to set up their operations across the districts.
From 2011 to 2015, the real GSDP of the state has increased significantly from aboutRs 3.9 lakh crore in 2011 to about Rs 4.9 lakh crore in 2015. The agriculture sector's share in the GSDP is about 29%, the industrial sector's share is about 19% while services sector's share in the state's GSDP has been recorded at 52%.
Speedy reforms aid growth
 The state government has taken various initiatives to create an environment that is conducive to development of infrastructure, industry, trade and commerce. To bolster manufacturing sector, the government has simplified the land acquisition process under which land could be sold through a simple agreement between the seller and the buyer.
The state government has taken various initiatives to create an environment that is conducive to development of infrastructure, industry, trade and commerce. To bolster manufacturing sector, the government has simplified the land acquisition process under which land could be sold through a simple agreement between the seller and the buyer.
The move would certainly pave the way for the development of infrastructure projects which were stalled due to stringent laws in the past. The state government has been striving to attract investments in Uttar Pradesh.
Accordingly, the state government has recently announced a special incentive package for units investing more than Rs 200 crore and a rebate of 25% on prevailingsector rates to investors.
Big push to highways, infra
The Agra-Lucknow expressway which is under construction is expected to provide vast opportunities for the food processing industry. The state government has been developing clusters in Noida and GreaterNoida for electronics manufacturing.
 The central government, on the other hand, under its National Highway DevelopmentProgramme (NHDP) has approved highway projects worth Rs 3,873.6 crore in the states ofOdisha, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh.
The central government, on the other hand, under its National Highway DevelopmentProgramme (NHDP) has approved highway projects worth Rs 3,873.6 crore in the states ofOdisha, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh.
An outlay of Rs 1,325.09 crore has been set aside for the four-laning of the Lucknow-Sultanpur section of NH-56 under NHDP phase-IV. This amount includes the cost of land acquisition, resettlement and rehabilitation and other pre-construction activities. The development of highways will help in uplifting the socio-economic conditions of the concerned regions of the state.
Moreover, it will also increase the employment potential for local labourers for project activities. The 302km-long Lucknow to Agra Expressway would be the country's longest access controlled six lane expressway.
The project would cost nearly Rs 15,000 crore of which Rs 11,526 crore would befor construction of the expressway and the rest for purchasing land at market rates. To facilitate ease of doing business in the state, the state government has launched a website on IT policy. The government has incorporated industrial services in the Janhit Guarantee Actwhich not only sets deadline for service delivery but also set up an appellate system if they are not met.
Simplified procedures
The UP government is also in the process of modifying its 'single window' clearance system for large sized investment proposals. The state has simplified procedures with speedy on line approvals through web-basedplatform called Nivesh Mitra.  High-level committees were formed to monitor the implementation of projects and a helpdesk from Uttar Pradesh Udyog Bandhu.
High-level committees were formed to monitor the implementation of projects and a helpdesk from Uttar Pradesh Udyog Bandhu.
UP is one of the first states to introduce 'single table' system and formulated its ownSEZ (Special Economic Zone) policy along with other industry-friendly policies. The state government has clearly defined guidelines for PPP projects for transparent bidding process with promise of profits and gains. For the conservation of environment, UP has launched the Green Belt Development Scheme under which initiatives will be taken to increase the total forest cover in thestate.
The UP government has prepared an action plan to boost solar energy and a policy has been implemented in this direction with efforts being made to add 13,000 MW to state capacity of 10,000 MW.
Going ahead, these reforms are expected to bring out desired outcomes which would pave the way for high and sustainable economic growth of the state in the coming times.
Progressive state budget
The UP budget for 2015-16 has accorded high priority to roads, irrigation and power sectors. A huge outlay of Rs 51,516 crore has been allocated for strengthening and development schemes of energy, irrigation, roads and bridges.
- Rs 17,871 crore has been allocated for roads and bridges
- Rs 25,764 crore for the power systems
- Rs 9,388.79 crore for new schemes

Further, on the socio-economic front, a provision of Rs 26,231 crore in the budget forScheduled Tribes, Scheduled Castes, OBCs, physically challenged and poor people of thegeneral category has been announced which would benefit them directly.
The budget has sanctioned Rs 2,776 crore for the minority welfare and Rs 300 crore for 8,000 homeless families. Provision for Rs 250 crore has been made for a new sugar mill of 3500 TCD capacity at Azamgarh, a cogeneration unit and 'Aswaani' plant in place of the closed cooperative mill at Sathiaon which would uplift the economic status of the cane growers.