Himachal Pradesh Economy
 A leader in hill area development, Himachal has diversified its industries with careful planning and strict implementation of policies reaping economic dividends.
A leader in hill area development, Himachal has diversified its industries with careful planning and strict implementation of policies reaping economic dividends.
The state has made rapid strides in select industries, power, horticulture, agriculture and allied activities over the decades.
The economy is poised to achieve a GDP growth of 6.5% in 2014-15.
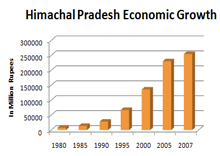
At current prices, the GSDP is estimated at Rs 85,841 crore in 2013-14 as against Rs 76,259 crore in 2012-13 showing an increase of12.6% during the year.
The per capita income (per capital GDP) at current prices witnessed an increase of 11.4% as it increased to Rs 95,582 in 2013-14 from Rs 85,792 in 2012-13.
The increase in total state domestic product is mainly attributed to 15.3% growth in the primary sector (agriculture); 9.8% in community and personal services; 2.6% in transport and trade; 4.5% in the finance and real estate.
Whereas the secondary sector (core industries) increased by only 2.6%.
The food grains production, which was 15.41 lakh MT during 2012-13, has increased to 15.76 lakh MT during in 2013-14.
It is expected to reach 16.20 lakh MT in 2014-15.
The fruit production has also increased by 55.8%, i.e. from 5.56 lakh MT in 2012-13 to 8.66 lakh MT in 2013-14.
And during 2014-15 (up to December 2014) the fruit production was 6.53 lakh MT.
Shift in economic priorities
 The economy has shown a shift from agriculture sector to industries and services.
The economy has shown a shift from agriculture sector to industries and services.
For, the percentage contribution of agriculture and allied sectors in total state domestic product (GSDP) has declined from 57.9% in 1950-51 to 55.5% in 1967-68; 26.5% in 1990-91 and to 14.25% in 2013-14.
The share of industries and services sectors respectively has increased from 1.1 and 5.9% in 1950-51 to 5.6 and 12.4% in 1967-68; 9.4 and 19.8% in 1990-91 and 18.40 and 42.85% in 2013-14.
The declining share of agriculture does not, however, affect the importance of this sector in the state's economy.
For the state GDP growth is still determined by the trend in agriculture and horticulture production.
It is the major contributor to the total domestic product and hasoverall impact on other sectors via input linkages, employment and trade.
Due to lack of irrigation facilities the agricultural production to a large extent still depends on timely rainfall and weather conditions.
High priority has been accorded to this sector by the government.
Expanding horticulture in Himachal Pradesh
 The state has made significant progress in the development of horticulture.
The state has made significant progress in the development of horticulture.
The topographical variations and altitudinal differences coupled with fertile, deep and well drained soils favour the cultivation of temperate to sub-tropical fruits.
The region is also suitable for cultivation of ancillary horticultural produce like flowers, mushroom, honey and hops.
In 2014-15 up to December 2014, 6.53 lakh tonnes of fruits were produced in the state.
As against the target of bringing 3,000 hectares of additional area under fruit plantation, the government has achieved 3,447 hectares in 2014-15.
Besides, 9.59 lakh fruit plants of different species were distributed up to December 2014 for the fiscal 2015.
12th Five Year Plan outlay in Himachal Pradesh
The aggregate size of the 12th Five Year Plan (2012-17) has been projected at Rs 22,800 crore.
However, the annual plan for 2015-16 has been proposed at Rs 4,800 crore which will be 9.09% higher than the plan size of 2014-15.
Bharat Nirman aiming towards the development of basic rural infrastructure like roads, irrigation, water supply, housing, rural electrification and telecom connectivity has been given top priority by the government.
To fulfil the commitments towards public, a separate department of redressal and public grievances under the direct supervision of the Chief Minister has been set up in each of the departments to make this more efficient.
Himachal Pradesh is the first state in the country to launch "e-samadham" for redressal of public grievances.