Laparoscopic surgery Procedures
 A video camera is inserted into one opening, which monitors and
guides the surgeon who is manipulating the instruments in the
other two openings. On the ends of these instruments are devices
such as scissors, surgical staplers, scalpels, and sutures
(stitches).As instrument moves along, the camera sends images to
a video monitor. Laparoscopy permitssurgeon to clearly see
inside patient’s body in real time, without open surgery.
Through laparoscopy, surgeon also can obtain biopsy samples
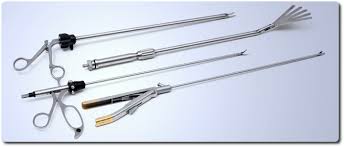
during this procedure. In this procedure, 5–10 mm diameter
instruments such as graspers, scissors, clip applier can be
introduced by the surgeon into the abdomen through trocars which
is the hollow tubes with a seal to keep the CO2 from leaking.
A video camera is inserted into one opening, which monitors and
guides the surgeon who is manipulating the instruments in the
other two openings. On the ends of these instruments are devices
such as scissors, surgical staplers, scalpels, and sutures
(stitches).As instrument moves along, the camera sends images to
a video monitor. Laparoscopy permitssurgeon to clearly see
inside patient’s body in real time, without open surgery.
Through laparoscopy, surgeon also can obtain biopsy samples
during this procedure. In this procedure, 5–10 mm diameter
instruments such as graspers, scissors, clip applier can be
introduced by the surgeon into the abdomen through trocars which
is the hollow tubes with a seal to keep the CO2 from leaking.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure
In general, abdominal laparoscopy has the following steps:
1. Once the patient is unconscious through injecting general anaesthesia, the surgeon makes a small cut near or at the navel and inserts a thin, hollow tube called a trocar. The tube extends from inside the abdomen to the outside.
Types of trocars:
- 10 mm trocar & cannula
- 5 mm trocar & cannula
- 3 mm trocar & cannula
2. Next step is to inject Carbon dioxide gas into the abdomen to expand it and allow the doctor more room to view the organs.
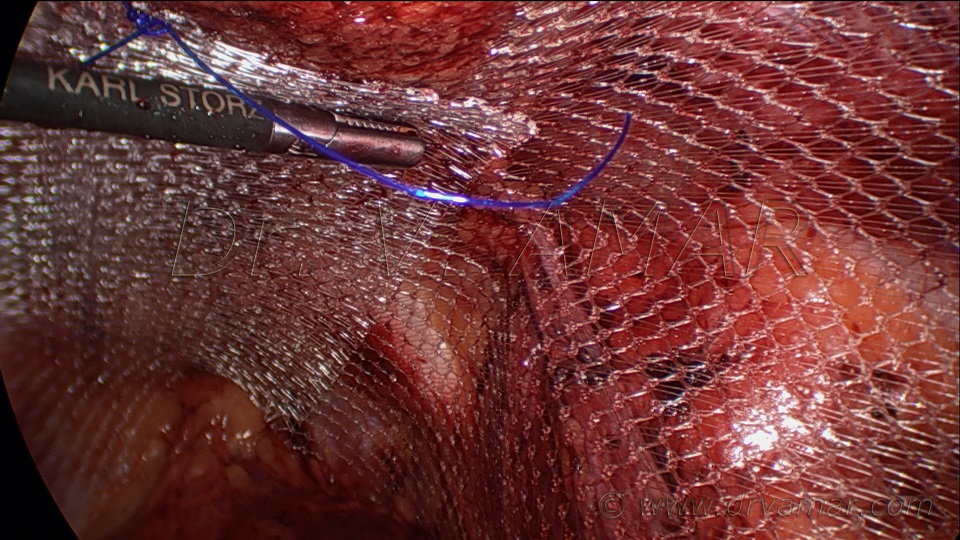
3. After that, the laparoscope, a medical instrument with a high-intensity light and very small camera, is inserted into the abdomen through the trocar. The surgeon is able to see a large image from the camera on a TV screen in the operation theatre.
Digital laparoscopic camera:
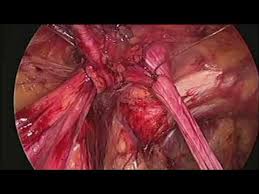
 4. Then other instruments to perform operation are inserted into
small openings. The surgeon manipulates these to perform the
procedure, whether they have to remove an organ such as gall
bladder, taking a sample of tissue, or repairing an organ.
4. Then other instruments to perform operation are inserted into
small openings. The surgeon manipulates these to perform the
procedure, whether they have to remove an organ such as gall
bladder, taking a sample of tissue, or repairing an organ.
5. When the surgery is completed, the surgeon removes all the instruments.
6. After that the incisions are stitched closed, and bandages are placed over them. For tiny incisions, there is no need of stitching. Surgeons only wrap with small strips of sterile tape.
When laparoscopy is used to diagnose a condition, the procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes. It takes more time if the surgeon treats a medical condition, depending on the type of surgery being performed.
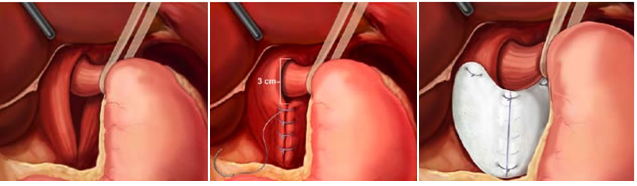
 For gall bladder removal through laparoscopy surgery procedure,
instead of a minimum 20 cm incision as in traditional (open)
cholecystectomy, four incisions of 0.5–1.0 cm isenough. Since
the gall bladder is similar to a small balloon that stores and
releases bile, it can usually be removed from the abdomen by
suctioning out the bile and then removing the deflated
gallbladder through the 1 cm incision at the patient's navel.
For gall bladder removal through laparoscopy surgery procedure,
instead of a minimum 20 cm incision as in traditional (open)
cholecystectomy, four incisions of 0.5–1.0 cm isenough. Since
the gall bladder is similar to a small balloon that stores and
releases bile, it can usually be removed from the abdomen by
suctioning out the bile and then removing the deflated
gallbladder through the 1 cm incision at the patient's navel.
There are some advanced laparoscopic procedures in which the size of the specimen being removed is too large to pull out through a trocar site therefore an incision larger than 10mm is made. The most common of these procedures are elimination of all or part of the colon (colectomy), or removal of the kidney (nephrectomy). Some surgeons perform these procedures completely laparoscopically, making the larger incision toward the end of the procedure for specimen removal, or, in the case of a colectomy, to also prepare the remaining healthy bowel to be reconnected (create an anastomosis). Other surgeons identify that since they will have to make a biggercut for specimen removal, they might use this incision to have their hand in the operative field during the procedure to aid as a retractor, dissector, and to be able to feel differing tissue densities (palpate), as they would in open surgery.
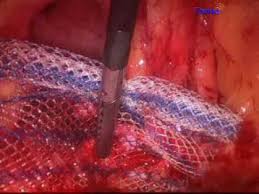 This procedure is known as hand-assist laparoscopy. Since they
will still be working with scopes and other laparoscopic
instruments, CO2 has to be maintained in the patient's abdomen,
so a device known as a hand access port must be used. Surgeons
who use this hand-assist technique feel that it decreases
operative time considerablyas compared to the straight
laparoscopic approach. It also supports and offers more options
to tackle unpredicted adverse events such as uncontrolled
bleeding that may require for creating a much larger incision
and converting to traditional surgical procedure.
This procedure is known as hand-assist laparoscopy. Since they
will still be working with scopes and other laparoscopic
instruments, CO2 has to be maintained in the patient's abdomen,
so a device known as a hand access port must be used. Surgeons
who use this hand-assist technique feel that it decreases
operative time considerablyas compared to the straight
laparoscopic approach. It also supports and offers more options
to tackle unpredicted adverse events such as uncontrolled
bleeding that may require for creating a much larger incision
and converting to traditional surgical procedure.
Recovery:
 After completing laparoscopy, patient is comfortable and
relieved from pain.Patient maybe mystified as hehas to recover
from the effects of the anaesthetic. It has been found that some
people feel sick or vomit. These are normal side effects of the
anaesthetic and normally disappears fast.
After completing laparoscopy, patient is comfortable and
relieved from pain.Patient maybe mystified as hehas to recover
from the effects of the anaesthetic. It has been found that some
people feel sick or vomit. These are normal side effects of the
anaesthetic and normally disappears fast.
In the recovery period, patient is under supervision of doctors and para medical staff. Nurse monitors the patient for a few hours until the patient is fully awake and able to eat, drink and pass urine.Before patient is discharged fromhospital, some important instructions about how to take care of wounds and when to come for a follow-up are given.
For a few days after the procedure, patient feel some pain and uneasiness where the incisions were made, and may also have a sore throat if a breathing tube was used. Generally, doctor prescribes painkiller medication to lessen the pain.
Some of the gas used to inflate patient’s abdomen can remain inside abdomen after the procedure, which can cause:
- Bloating
- Cramps
- Shoulder pain, as the gas can irritate diaphragm, which in turn can infuriate nerve endings in patient’s shoulder
 But all these symptoms are normal in laparoscopic surgery and
patients should not worry about these medical conditions as
symptoms disappears in a day or two when body absorbs the
remaining gas.
But all these symptoms are normal in laparoscopic surgery and
patients should not worry about these medical conditions as
symptoms disappears in a day or two when body absorbs the
remaining gas.
Basically, in laparoscopic surgery, all the procedures were initially developed as open surgery methods. Since the laparoscopic surgery is continuously evolving, surgeons use new instruments to perform operations.

Articles on Health
- Laparoscopic Surgery Advantages
- Laparoscopic Surgery History
- Laparoscopic surgery Procedures
- Limitations of traditional laparoscopic surgery
- New technologies for advance laparoscopic surgery
- Non-Robotic Laparoscopic Surgery
- Robotic Laparoscopic Surgery
- Causes and remedy for dark circles in females

- Harmful impact of mobile phone on unborn baby

- Maternal health care tips

- Rheumatoid Arthritis is Most Widespread in Female
- Periodontal ailment during Pregnancy
- Anemia is prevalent in Women
- Effect of Cell phone tower radiation on human health

- Current health scenario india
- Government health policies india
- Medical facilities india
- Hospital infrastructure india
- Shortage of Medical Professionals in India
- Quality standards indian hospitals
- Indian states health statistics
- Medical expenses india
- Hospitals in Ahmedabad
- Hospitals in Bangalore
- Hospitals in Chennai
- Hospitals in Cochin
- Hospitals in Delhi
- Hospitals in Hyderabad
- Hospitals in Kolkata
- Hospitals in Mumbai
- Hospitals in Pune
- Hospitals in Coimbatore
- Hospitals in Kochi
- Orthopaedics Hospitals in India
- Diabetology Hospitals in India
- Cardiology Hospitals in India
- Infertility Hospitals in India
- Neurology Hospitals in India
- Paediatrics Hospitals in India
- Nephrology Hospitals in India
- Oncology Hospitals in India
- Antiaging foods to improve skin

- Tips for Maintaining healthy bones
- Guidelines for preventing heart disease
- Tips to reduce eye strain while working on computer
- Mental health problems among elderly people
- Health problem of piles

- Health advices for air travel

- Dealing with Allergies
- Tips for Eyes Care
- Care for Crystal Clear Skin
- Tips For Healthy Hair
- Healthy Living is The Absolute Measure of Happiness
- Let Fragrance Rule Your Summer
- Most common vestibular disorder

- Osteoporosis Risk Factors
- Dengue

- Endocrine disorder

- Causes of liver damage
- Dry eye syndrome
- Kidney Stones
- Conjunctivitis: Irritating eye disease
- Anxiety Disorder
- Causes of Brain Damage
- Hepititis B
- Knowledge of Osteoarthritis
- Mental Illness
- Back Pain
- Sugar Addiction
- Diet Control Plans
- General Motors Diet Plan
- No Carbohydrate Diet
- One day Diet Plans
- Seven day diet Plans
- Vegetarian Diet
- Food for Health
- Genetically Modified Foods
- Healing Effects Of Fruits
- Vegetables That Heal
- Healing Effects Of Spices and Herbs
- Test your Stress Level
- Mantras for Relaxation & Stress free life
- Take walk For a healthy body and mind
- Squint is frequently observed in Children
- Consult-Doctor
- Free Handy Health Advice