About of Nagaland
Nagaland is a landlocked State in the Northeast of India. It is among the smallest states in India. Chubi , Dhansiri, Doyang and Dikhu are the main rivers flowing through the state of Nagaland whose terrain is mountainous. With a height of 12,600 ft above seas level, the Saramati peak in the Twensang district is the highest point in the state. Nagaland experiences heavy rains. The average rainfall is between 1800 to 2500 mm (70 to 100 inches) a year.
Geography Of Nagaland
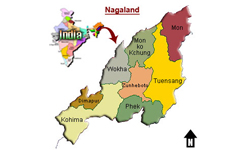
Located in the Northeast region of India, Nagaland shares its border with Arunachal Pradesh on the north, Assam on the west, Manipur on the south and Myanmar on the east. Nagaland has four soil types: Inceptisols, Ultisols, Entisols and Alfisols. These types of soils support a variety of agricultural crops like paddy, maize, potato, sugarcane and tea.
Economy Of Nagaland
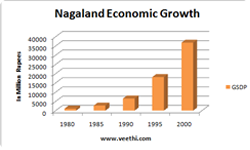
Cultivation of bamboo is carried on a large sale in Nagaland whose bamboo growing stock account for 5 per cent of the total stock in India. During the 12th Five-Year Plan, which is valid from 2012 to 2017, the state plans to increase its raw silk production from 619 MT in 2014-15 to 1,700 MT by 2017.
Infrastructure Of Nagaland

Nagaland is well connected with Assam and Manipur through five National Highways (NH)- NH-40, NH-44, NH-51, NH-62 and NH-127B. In 2014-15, the total length of Nationals Highways in Nagaland was 1,080.09 km. In the 2015-16 budget, the state government had proposed to allocate US$ 14.1 million to maintain the existing roads and infrastructure. Agencies responsible for the maintenance of roads in the state are the Public Works Department (PWD) and Sewak (a Border Roads Organization of the Government of India). Nagaland State Transport provides state road transport services, operating its vehicles on 112 routes and covering 21,300 km daily.